How Cancer Cells Steal Energy to Survive and Spread?
Posted 1 month ago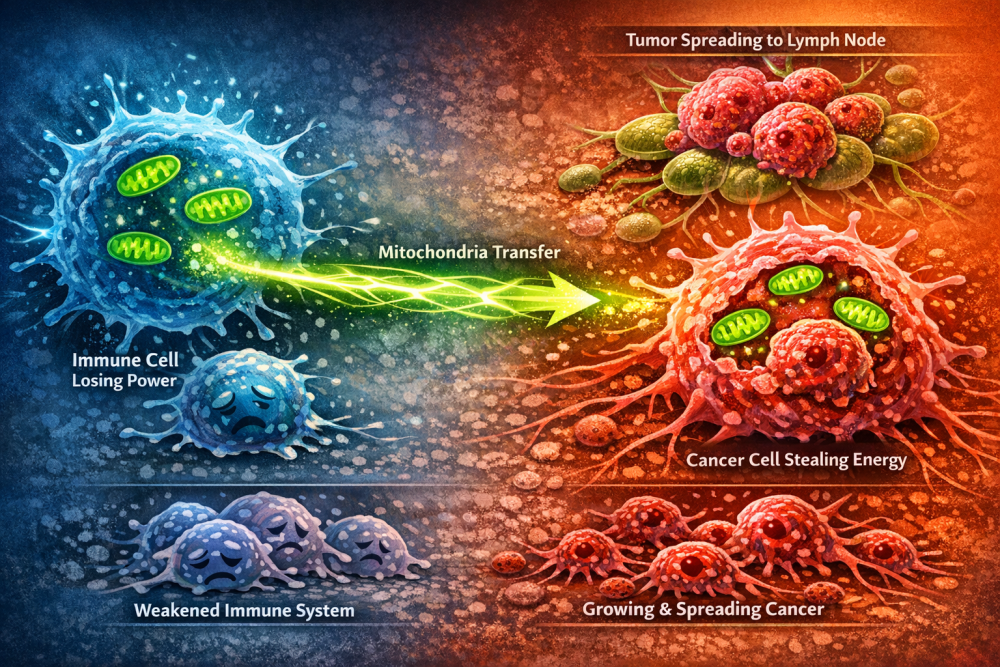
2/2026
Cancer isn’t just a mass of uncontrolled cells; it also fights against your body’s defenses. Scientists have long known that the immune system tries to detect and eliminate cancer, but a new discovery suggests that some tumors might have an unexpected trick: they steal energy from immune cells, thereby weakening them and preventing them from doing their job.
🔋 What Are Mitochondria and Why Do They Matter?
Inside all our cells are tiny structures called mitochondria, often nicknamed the powerhouses of the cell. They generate energy that cells need to survive and function properly. Immune cells, especially those fighting infections or tumors, rely heavily on mitochondria to power their activities.
🦠 Cancer’s Sneaky Strategy
According to new research reported in Nature:
👉 Some cancer cells can acquire mitochondria from nearby immune cells, similar to stealing batteries from a rival team (This study was conducted in a mouse model).
Here’s what seems to happen:
- Cancer cells interact with immune cells that try to attack them.
- Instead of merely defending themselves, cancer cells hijack the mitochondria from these immune cells.
- The result? The immune cells weaken because they lose their energy engines, while the cancer cells gain extra power.
This “mitochondrial theft” could help tumors evade immune responses and spread more easily. One part of the study even showed that this facilitates tumors infiltrating lymph nodes, which are critical hubs of the immune system.
🧠 Why This Discovery Matters
This idea is striking because it flips our assumptions about how cancer and immune cells interact:
✔ Scientists used to think that cancer cells mainly hide from immune detection.
✔ Now, this study shows they might also hijack energy directly from immune cells, weakening the body’s response and helping them survive.
If this mechanism also exists in humans (not just in mice), it could explain why some tumors resist immune-based therapies and continue to grow despite treatment.
🧪 What This Means for Future Science and Medicine
These scientific findings:
🔹 Provides a new clue about how cancers evade immune attack.
🔹 Could lead to innovative treatments that stop this mitochondrial theft, improving immune cells' chances of success.
🔹 May help explain why some cancers spread so fast.